Introduction
Are you planning to set up an international franchise for your business?
Do you want to leverage the international market for your business?
If your answer to any of the above questions is a definite yes! Then, welcome to Legamart’s ultimate guide to understanding taxation in the international franchise in 2022, where we provide an in-depth explanation of the various models of the franchisee, the documents you need to establish an international franchise, and most importantly, how to understand and handle tax in the international franchise. So, let’s get started!
What is a franchise?
A franchise is an arrangement between an existing business and a new entrant of the same business model. The franchise is an authorized user of the brand’s reputation by getting permission through a license. The franchisor is the business owner who grants the license, and the franchisee is the license holder. The main motive of this arrangement is to share profits and royalties between the franchisor and franchisee. The franchisor gets license fees, and the franchisee establishes a business under the name that already has a reputation and value in the market.
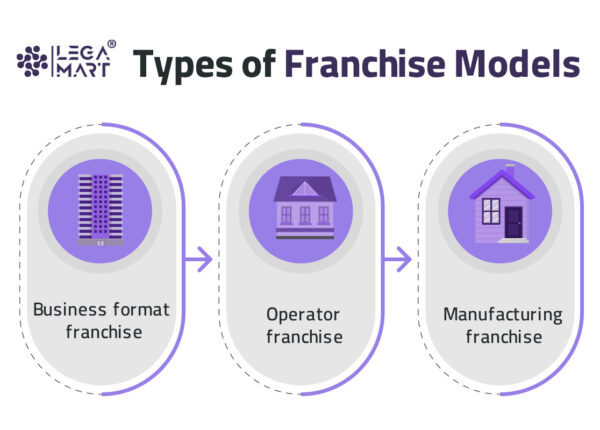
Each business arrangement is unique. Following are some standard franchising models:
Business format franchise
A franchise with a distribution network that operates under a common trademark or trade name, with franchisees paying the franchisor for the right to do business under that name for a certain period, is called a business format franchise. In exchange, the franchisee is granted permission to utilize the franchisor’s entire business system or format, including the brand, goodwill, products and services, operational manuals and standards, marketing methods, systems, and support facilities. In turn, the franchisor is obligated to provide initial and continuing services and support.
This franchise model comes with all the recognition and brand value. A franchisee can obtain it in exchange for a license fee or royalty. The fast food industry is a good instance.
Operator franchise
This franchising concept gives franchisees control over business operations. This ownership structure is ideal for investors who desire full control over their investment and operational decisions. The time commitment may be higher, but it’s suitable for job changers or business owners who want to be engaged in everything. This model is ideal for first-time franchise owners since it will help them understand the brand’s operations from the ground up and confidently lead the team to success with the franchisor’s assistance. Owner-operators are more frequent than absentee and semi-absentee franchise owners.
Manufacturing franchise
The franchisor in a manufacturing franchise permits a franchisee to make things under their brand name and trademark. This type of franchise is typically found in the food and beverage industry. A soft drink corporation is the finest illustration of this. The parent business will manufacture the concentrated syrup and then sell it to a bottling company, along with the right to utilize its brand name and trademarks. The syrup will then be mixed with water and bottled before being sold to multiple vendors by that firm.
Franchising in the international market
The sole purpose of any business is to generate more revenue and have the best recognition. Companies and businesses have turned to international expansion to achieve this purpose. Businesses expand overseas to increase global representation as well as earn profits.
And the prospect of being the sole owner of a series of profitable franchises in a nation is appealing to investors. McDonald’s, Marriott, and Hertz are a few examples of household names that have significantly benefited from worldwide franchising.
International franchising, also known as international licensing, enables innovative enterprises to expand into new markets by leveraging their brand and intellectual property (trademarks and know-how) in exchange for royalties and product sales.
With low-risk incentives, this type of strategic cooperation promotes enterprises to expand globally. It takes relatively minimal up-front investment for the franchisor because the franchisee must meet the financial requirements in exchange for the keys to the firm. In exchange, the franchisee has unique access to an established brand and demonstrated know-how. Of course, when it comes to new enterprises, there are no promises. On the other hand, having the continued assistance of the franchise headquarters in your rear pocket is a valuable benefit. The franchisee’s success is in both parties’ best interests.
Hence, to get into such a franchise, foreign businesses enter into agreements with some local person and grant licenses for the operation of the business in their jurisdiction.
They enter into franchise agreements with them and expand internationally. Following are some types of agreements that parties can go for to confirm their franchise -:
Direct franchise agreement
Direct franchising is the simplest and most popular method of establishing a franchise business. The franchisor and franchisee sign the franchise agreement directly. The franchisor offers the services indicated in the franchise agreement to the licensee and performs all operations necessary for the firm to run smoothly. It also provides continuing help and guidance, educates staff, and engages in marketing, advertising, accounting, and financial operations.
When a franchisor establishes a franchise system remote from the headquarters (for example, abroad or in another geographic location), it might not be easy to maintain control over the franchisee and offer continuous services. It is prudent to consider delegating part of their authority to an intermediary. Using a multiple franchise, master franchise, or regional representative office, for example.
Master franchise agreement
A master franchise agreement is the most typical form of international franchise nowadays. This is more of a territorial strategy in which the franchisor offers the franchisee exclusive rights to build the brand in another nation, state, or territory. The franchisee gains extraordinary access to a well-known brand and has the opportunity to capture a market share in the new location immediately. For the franchisor, having a local individual with local expertise take personal responsibility may minimize potential political and regulatory challenges in an unknown location more readily – and even helps to save expenses and risks associated with studying a new territory.
A master franchise agreement requires the franchisee to pay a higher-than-usual startup cost to obtain exclusive rights to a particular territory. The master franchisee will be required to open several regional operational units over a set time. Another advantage of becoming a master franchisee is attracting additional franchisees in their area. In other words, the master franchisor serves as the company’s central connection.
Advantages of international franchise
Exposure to new markets with a solid brand
International franchising has several benefits. Due to brand recognition and trust, one may reach more customers and sell more items and services with less effort in different parts of the world. An international network can aid with legal concerns or queries. It also benefits from modern technologies.
Ability to Adapt
It is critical to adapt to consumer trends to thrive in business. This entails remaining current with market research and adjusting to new trends. To address the demands of clients, an international franchise firm must have a budget and resources to begin and the capacity to undertake due diligence via market study.
Increased productivity and efficiency
International franchising has several advantages in terms of efficiency and production. International franchise may swiftly develop their business and hire the finest Metabase alternative that will both increase the business and try to decrease expenses with the help of a parent firm.
Disadvantages of having an international franchise
Compliance issues
Cultural differences may cause problems with branding, public relations, and business culture, but regulatory variations can also be challenging. Business laws and regulations can differ significantly between countries, provinces, and states, and these differences may affect every aspect of your business, including human resource policies, employee rights and benefits, and even the ingredients you can use to formulate your products. Plan on establishing distinct legal and compliance teams for your overseas operations.
Financial risk
Business owners must consider financial risks while growing abroad. Currency exchange rates may lower your investment return. Other countries may also have trouble receiving the goods and products you need. Shipping items into certain nations may incur customs and fines, hurting your company.
Taxing in international franchising

Taxation is an essential process in establishing a valid legal franchise. While establishing an international franchise, it is implied that the agreement should mention which tax regime is applicable and how parties to this agreement will pay taxes.
Taxing in an international franchise is usually a multi-jurisdictional and interconnected web. Various teams, professionals, and experts are involved in deciding upon the tax regime of business governance. It involves treaties, orders, and regulations from time to time. Parties must decide the jurisdiction, time frame, and policy for filing taxes in advance.
The international franchise tax is not the same as income tax. Instead, it is an extra amount imposed on a corporation apart from income and corporate taxes.
Many countries have proper laws that govern international franchise taxation and establishment in their jurisdiction. While in some countries, it depends upon the nature of the agreements and contracts entered by the parties.
Franchise taxes are levied on corporations, business partners, and overseas LLCs. They have to pay taxes as per the jurisdictions in which they operate.
Non-profits, unincorporated organizations, and political groups are not subject to franchise taxes. It is, therefore, critical to understand the nature of a business before making a tax system, for example, a joint venture or partnership.
Things to consider in international franchise tax
For a franchise, various compliance issues must be addressed in the International franchise setup. These include following transfer pricing guidelines, managing withholding taxes on payments to foreign franchisees, utilizing double taxation treaties to avoid overlapping tax liabilities, considering the implications of a potential permanent establishment, navigating diverse VAT/GST and sales tax regulations, fulfilling local reporting mandates, securing necessary registrations and licenses, maintaining comprehensive documentation, and complying with anti-avoidance rules. Collaboration with foreign taxation professionals is critical to ensuring rigorous compliance and operational performance. There are a few things that you should take into note when agreeing to taxes in an international franchise.
Rent, service, royalties, interest
Royalties, rentals, service fees, and interest may be withheld by the foreign nation from the International/foreign franchisor.
The franchise agreement should require the FC Franchisee to pay all foreign taxes on U.S. Franchisor payments to safeguard the U.S. franchisor.
For further insights into protecting your brand globally, explore our guide on ‘How to Trademark a Logo in the USA‘ for essential steps in securing your logo’s legal identity.
Tax Treaties
Tax treaties decrease or eliminate withholding taxes. Understanding whether payments are free from withholding tax under a tax treaty or the foreign country’s tax rules and arranging a franchise agreement might save considerable tax.
Other countries may levy sales-and-use or value-added taxes on FC Franchisee payments for goods and services or rental payments in addition to withholding taxes. These taxes must be considered.
Taxation in international franchise in the US

Franchise tax rates and exemptions vary from state to state in the US. Such as Alabama, Arkansas, California, Delaware, Georgia, Illinois, Louisiana, Mississippi, New York, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Texas have franchise taxes. In contrast, Kansas, Missouri, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia eliminated corporation franchise taxes in their states.
Following are the few franchise tax rates imposed by the states in the US:
Delaware franchise tax Rates
Delaware franchise tax rates range from $175 to $250,000 annually, depending on company size and filing method. Limited partnerships (LP), LLCs, and general partnerships in Delaware pay just $300 in annual taxes.
Franchise taxes in California
In California, their small business taxes include a franchise tax. The California company franchise tax is $800 or 1.5% of net revenue. The LLC franchise tax is $800. LLP and LP franchise fees vary, but both must pay a minimum $800 franchise tax. LLCs that want to be taxed as corporations pay California’s corporate income tax rather than franchise tax. Franchise tax in California is taken care by Calfornia franchise tax board.
Also, a firm with multiple branches and locations may have to pay franchise taxes in all its registered states. Franchise and other state business income taxes do not apply to sole proprietorships since they are not registered with the state.
Is the franchise subjected to double taxation?
The tax laws of the countries and any relevant tax treaties determine whether a franchise is double-taxed or not. Double taxation occurs when multiple countries tax the same income or profit.
International tax treaties, often double taxation treaties, are agreements between two nations outlining the regulations for taxing income and profits that transcend international boundaries. These treaties often contain measures to avoid or mitigate double taxation.
Potential sources of revenue for a franchise that might be taxed in various jurisdictions include:
- Franchise fees, royalties, and other payments made by the franchisee to the franchisor may be subject to withholding tax in the franchisee’s home country. Tax treaties often address the rates of withholding tax on such payments.
- If the franchise includes a physical presence or permanent establishment in another nation, the profits earned by such business may be taxed in that country.
- Also, if the franchise includes intellectual property, such as trademarks or patents, the revenue generated by this property may be taxed in both the franchisor’s and franchisee’s nations.
Tax treaties often include determining which nation has the central authority to tax certain kinds of income. They may also include measures for avoiding double taxation, such as granting a credit for taxes paid in one nation against taxes owed in another.
To evaluate if double taxation may apply and how it might be minimized, it is essential to thoroughly study the relevant tax treaties between the countries concerned and consider the structure of the franchise arrangement.
Conclusion
Operating in a franchising business is advantageous for both parties in a business arrangement. If all the formalities and documents are in the correct order, it is an excellent way for small investors to work under large umbrellas of brands.
A franchise gives the liberty to the franchisor to start a readymade business. It does not have to care about reputation and market value, as everything about the brand has already been established. While the franchise holder gets to explore international markets, earn globally, and have a powerful presence. This system of business allows the investors to have a diversified investment portfolio and representation in the international market.