“I’m originally from the UK and want to file an international patent application for my new invention in Turkey. However, I’m unaware of the patent cost in Turkey and how I can obtain a patent there.”
Patents are invaluable assets in the world of innovation, offering legal protection and exclusivity to inventors and businesses, an area frequently intersecting with Cross-Border & International Law. In Turkey, where technological advancements and entrepreneurial spirit thrive, understanding the intricacies of patent costs is paramount. This article will look into the dynamic realm of patent cost in Turkey, shedding light on the factors that influence expenses, the processes involved, and the significance of investing in intellectual property protection. Patents are invaluable assets in the world of innovation, offering legal protection and exclusivity to inventors and businesses, an area frequently intersecting with Cross-Border & International Law. In Turkey, where technological advancements and entrepreneurial spirit thrive, understanding the intricacies of patent costs is paramount. This article will look into the dynamic realm of patent cost in Turkey, shedding light on the factors that influence expenses, the processes involved, and the significance of investing in intellectual property protection.
Patents and Trade Secrets: The Best Way to Protect Your Business
What is a patent, and what does it protect?
In general terms, a patent protects new inventions for a certain period. It provides the inventor with the right to use or sell their invention in the commercial market, and it also gives the right to take legal action against the person who infringes the inventor’s rights by using the invention without the permission of the actual owner.
In Turkey, the Decree Law numbered 551 and dated June 24th 1995, on the Protection of Patent Rights (the Decree-Law) aims to protect inventions by granting patents.
In Turkey, an invention qualifies for a patent if the following factors apply:
- Novelty: The term “novelty” means an invention that is new to the world and is not mentioned in any document or registered worldwide.
- Inventive Step: Inventive Step means the invention should be non-obvious to the person who is an expert in that particular field. The invention should not be ordinary or evident if it is a known technology.
- Industrial Application: The invention should be capable of Industrial application. For example, it is possible to manufacture and create a pen again. Then, it is capable of being industrially applicable. If the same pen cannot be manufactured multiple times, it cannot qualify as industrially applicable.
In Turkey, the patent offers protection for 20 years, subject to examination. Patent protection can be registered in two ways: with or without examination. Without examination, patents are protected for seven years. In the rapidly evolving global marketplace, Turkey has positioned itself as a key player, attracting both domestic and international investors. Given its strategic location bridging Europe and Asia, along with its growing economy, the country has seen an influx of innovative ideas and technologies. In this context, patent registration in Turkey becomes crucial. Securing a patent not only safeguards the rights of the inventor but also fosters an environment where creativity and innovation are rewarded. Read more about the benefits of patenting registration on our legamart blog!
Types of patent in Turkey
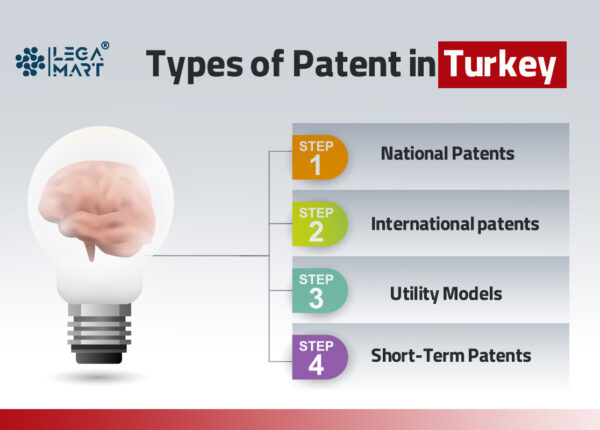
There are four types of patents according to the Decree-Law 551in Turkey –
National patents: National patents may be filed in Turkey and registered with the Turkish Patent and Trademark Office (TurkPatent) for 20 years. Opposition to national patents may be filed within six months of the grant decision being published in TurkPatent’s official patent bulletin.
International patents: These are valid for 20 years from the date of application. This allows foreign innovators to seek protection for their inventions in Turkey.
Utility models: Utility Models: To qualify for a grant in Turkey, utility models must be unique and have industrial applications rather than fulfil the requirements for an inventive step. Utility Models are protected for ten years from the date of filing.
Short-term patents: Previously, short-term patents may be awarded for seven years without a substantive review under Decree-Law 551, which safeguarded patents. The current IP Code has repealed the short-term patent rules. However, prior Decree-Law patents remain valid and enforceable.
Patents and Trade Secrets: The Best Way to Protect Your Business
Process of filing a patent in Turkey

To be patented, inventors must follow the following procedure in Turkey:
Application: The inventors must submit a patent application to the Turkish Patent and Trademark Office (TPTO) with the invention’s claim, specifications, and drawings.
Examination: After receiving the inventors’ application, the TPTO checks the patent for novelty, ingenuity, and industrial utility. After the TPTO has evaluated and accepted the inventor’s application, the patent is published in the Official Patent Bulletin.
Opposition Period: Interested parties have a defined amount of time to object to the published documents. Application for a Patent
Grant: The patent is granted to the inventor if no legally binding duties grant them exclusive rights to the invention for a certain period.
Patent enforcement legal procedures
To have their rights enforced against infringers, patent owners may bring infringement actions in Turkey before specialised Intellectual Property Courts. These proceedings usually begin with a preliminary injunction claim and include the following procedures:
Preliminary Injunction: The patent owner may seek a preliminary injunction to prevent future infringement before the trial. Steps like this help to preserve evidence and defend the patent owner’s rights.
Evidence gathering: Both parties must provide papers, witnesses, and expert testimony throughout the trial to substantiate their arguments.
Judgement Phase: The court decides based on the claims and evidence.
Infringement actions extend beyond patent violations to encompass trademark and copyright infringements, along with other forms of infringement. The specific type of infringement depends on the nature of what has been copied or violated, such as formulas, music, tangible items, or other creative content.
How much does a patent cost in turkey versus other countries?

The official patent costs in Turkey are revised and released each year at the beginning of the year, and they take effect on January 1st.
Recently, the Turkish patent and trademark office for patents and utility models established a new official patent fee, increasing by 36%.
In Turkey, the current official fees for patent protection are as follows:
The official cost for protecting the European Patent applications is 1.930 TRY
- Validation of European patents costs 3.095 TRY
- PCT national entries cost 2.015 TRY
- Patent applications cost 75 TRY
- Utility model applications cost 75 TRY
Compared with the foreign currencies, the official fees released in 2022 Turkey is lower but significantly higher than the previous year, i.e., 2021. The prices have increased because Turkish currencies suffered a significant loss against foreign currencies last year due to high inflation.
For more details regarding the patent fees, you can go through the official website of the Turkish patent and trademark office.
Conclusion
In Turkey, a patent grant is impossible if the invention does not fulfil the abovementioned criteria. However, to determine if the invention achieves the same, a proper examination is conducted to ensure it is patentable. However, a fee is involved in every procedure, which differs in different countries.
As compared to other countries, Turkey has a lower patenting cost. However, it is not specific as every year, the official fees get revised, and the new official prices get released at the beginning of the year. Currently, the patent costs in Turkey are still lower than others but higher than the previous year’s official fees. Therefore, a minimal fee is required to register for a patent, and patents are not available for free.
Once a patent is successfully registered in Turkey, the inventor unlocks a new realm of possibilities through patent licensing agreements. A patent license agreement is a legally binding contract that allows the patent owner to grant specific rights to another party to use, manufacture, sell, or distribute the patented invention. Such agreements enable inventors to collaborate, expand their reach, and monetize their creations without the constant fear of unauthorized replication or misuse.
LegaMart is a global legal platform designed to connect individuals, startups, and businesses with qualified lawyers across jurisdictions. With a mission to simplify cross-border legal services, LegaMart provides users with access to a diverse network of vetted legal professionals who specialize in areas such as international law, corporate law, immigration, dispute resolution, and more.
By leveraging technology and user-friendly tools, LegaMart allows clients to search for lawyers by country, language, or legal expertise, submit their legal queries, and receive tailored legal solutions in a streamlined, efficient manner. The platform serves as a bridge between legal professionals and clients who need multilingual, multi-jurisdictional support — especially in today’s increasingly globalized legal landscape.
Whether you’re an entrepreneur launching a business abroad, an individual dealing with immigration paperwork, or a company navigating cross-border compliance, LegaMart aims to make legal help more accessible, transparent, and collaborative.