Introduction
Over the past decade, the rise of cryptocurrency has led to a new form of sanctions being implemented by governments and international organizations worldwide. These crypto sanctions, rooted in the evolving landscape of Cross-Border & International Law and Legal Practice & Specialization, have become a key tool in the foreign policy and national security strategies of several countries.
This article provides an overview of crypto sanctions, their impact on international trade, the crypto market, national security and foreign policy, case studies, challenges and criticisms, and the future of crypto sanctions.
Crypto sanctions: Background and overview
Crypto sanctions are a form of economic sanction that targets cryptocurrency users to facilitate transactions between sanctioned entities or individuals. These sanctions are typically imposed by governments or international organizations and are designed to limit the ability of sanctioned parties to access financial systems and engage in international trade. This is not a new concept, and they have been used since at least 2018.
The US Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) has been the most active agency in implementing crypto sanctions. However, other countries have started using them as well. In 2020, the European Union introduced its first-ever crypto sanctions against six individuals and three entities from Russia, China, and North Korea. Similarly, the United Kingdom introduced crypto sanctions against 22 individuals involved in human rights violations in various countries.
Crypto sanctions have become an increasingly important topic in the international community as the use of cryptocurrency has grown. With the potential for cryptocurrencies to circumvent traditional financial systems, the use of crypto sanctions has become an important tool for governments to maintain control over their economies and exert pressure on other nations.
Unlike traditional sanctions that target banks, financial institutions, and other physical assets, crypto sanctions target virtual assets. This means governments can target individuals, entities, or countries operating exclusively in cryptocurrencies. Using crypto sanctions is a game-changer in international relations, as it allows governments to exert influence on actors that were previously beyond their reach.
Crypto sanctions: The basics
What are crypto sanctions?
Crypto sanctions are financial restrictions that target virtual assets like cryptocurrencies. These sanctions may prohibit individuals or entities from trading, holding, or transferring specific cryptocurrencies. They may also prohibit individuals or entities from engaging in transactions with specific individuals, entities, or countries involved in activities deemed harmful to national security or foreign policy interests. These sanctions are typically designed to limit the ability of these parties to engage in financial transactions or access traditional financial systems.
Types of crypto sanctions
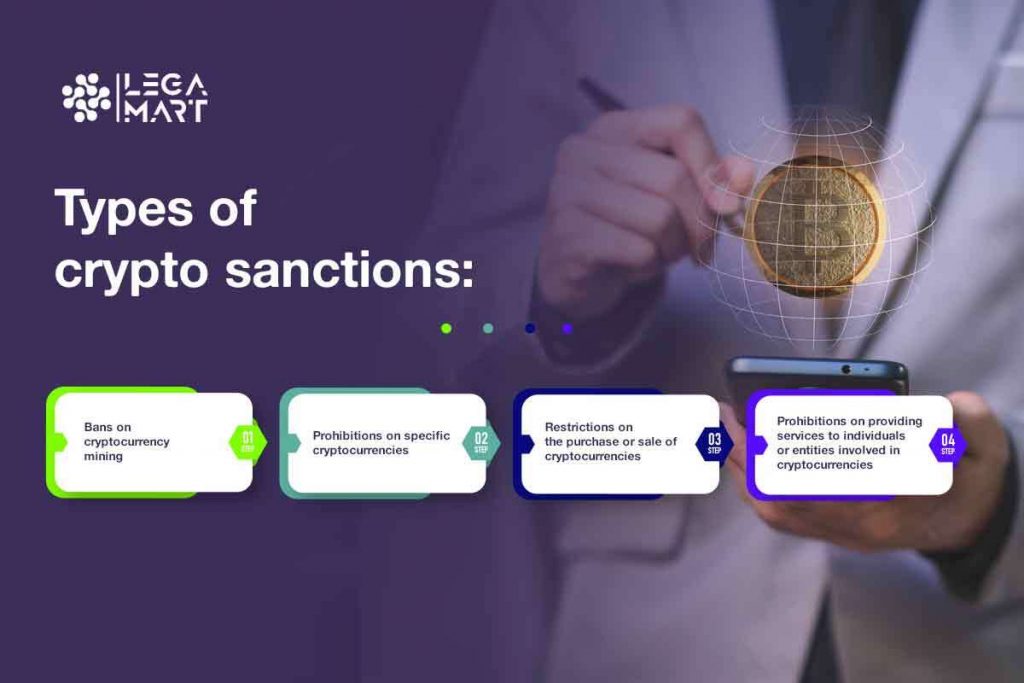
There are various types of crypto sanctions, and they may include the following:
Bans on cryptocurrency mining, for example, in May 2021, China banned Bitcoin mining in some regions, citing concerns over energy usage and financial risks.
Prohibitions on specific cryptocurrencies, such as in 2021, Nigeria’s central bank banned financial institutions from dealing with or facilitating transactions in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, citing concerns over their use in illegal activities and the lack of regulation. Also, in 2018, the Indian government declared that cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin were not legal tender and warned citizens against investing in them.
Restrictions on the purchase or sale of cryptocurrencies, like Turkey’s central bank, banned using cryptocurrencies for payments and prohibited payment providers from offering fiat-to-crypto onramps in 2021.
Bans on crypto exchanges or wallets, the Venezuelan government ordered the closure of all crypto exchanges and banned using cryptocurrencies as a payment method in 2018.
Prohibitions on providing services to individuals or entities involved in cryptocurrencies, for example, in 2019, the Central Bank of Egypt warned banks and other financial institutions against dealing with or providing services to individuals or entities involved in cryptocurrencies.
How do crypto sanctions work?
Crypto sanctions work by restricting the ability of sanctioned parties to access financial systems and engage in international trade in the same way as traditional sanctions, with the difference being that they target virtual assets. This is typically done by targeting the use of cryptocurrency as a means of circumventing traditional financial systems. Sanctions can be imposed on specific cryptocurrencies or the use of all cryptocurrencies.
In addition, governments may impose sanctions on individuals, entities, or countries involved in activities deemed harmful to national security or foreign policy interests. These sanctions may be imposed by individual countries or international bodies like the United Nations.
Examples of crypto sanctions
One such example of a crypto sanction is when the US government imposed crypto sanctions on various individuals and entities, including North Korea, Iran, and Venezuela. In 2018, the US government imposed sanctions on North Korea’s Lazarus Group, a state-sponsored hacking group involved in cryptocurrency theft. In 2019, the US government imposed sanctions on two Iranian nationals involved in a ransomware scheme targeting cryptocurrency exchanges.
In 2020, the US government imposed sanctions on the Venezuelan government’s Petro cryptocurrency, which was launched in 2018 as a way to circumvent US sanctions. There are various other countries which imposed such obligations, like Petro by Venezuela, the restriction of cryptocurrency mining in Iran, and the use of cryptocurrency theft by North Korea to fund its nuclear program.
Implications of crypto sanctions
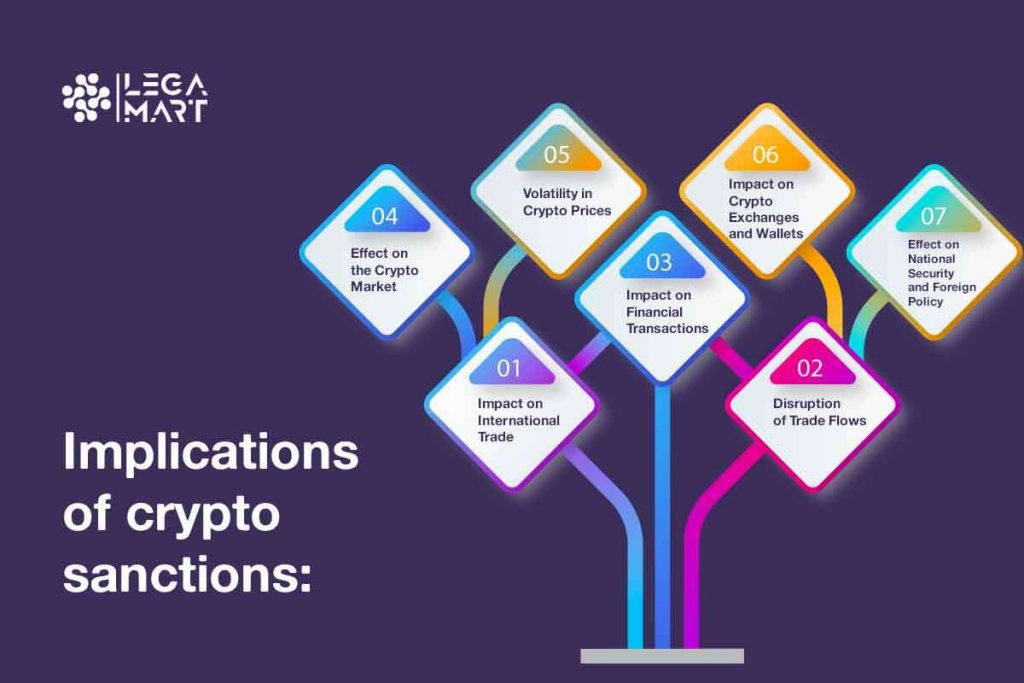
There can be several implications of crypto sanctions, such as:
Impact on International Trade
Crypto sanctions can significantly impact international trade by disrupting trade flows and limiting the ability of sanctioned parties to engage in financial transactions. This can lead to a reduction in trade volumes and an increase in the cost of doing business. Impact on international trade can include-
Disruption of Trade Flows
Crypto sanctions can have a significant impact on the trade flows of a country. These sanctions can disrupt trade flows by limiting the ability of sanctioned parties to engage in financial transactions. Leading to delays in the processing of transactions and an increase in the cost of doing business. Countries that rely heavily on cryptocurrencies for trade may be adversely affected if sanctioned. For instance, if a country is sanctioned and its national currency is restricted, it may be forced to rely on cryptocurrencies to conduct trade. In such a scenario, crypto sanctions may lead to a disruption in the trade flows of the country.
Impact on Financial Transactions
Crypto sanctions can also impact financial transactions between countries by limiting the ability of sanctioned parties to access traditional financial systems. This can lead to a reduction in the availability of credit and other financial services and an increase in the cost of doing business. If a country is sanctioned and its access to financial institutions is restricted, it may turn to cryptocurrencies for financial transactions. However, using cryptocurrencies for such transactions may be subject to sanctions, leading to a total disruption in financial transactions.
Effect on the Crypto Market
Quite naturally, the sanctions on Crypto affect the crypto market badly. These significantly impact the crypto market by creating volatility in crypto prices and limiting the ability of sanctioned parties to access crypto exchanges and wallets.
Volatility in Crypto Prices
Crypto sanctions can lead to increased volatility in the crypto market. For example, if a country is sanctioned and its use of cryptocurrencies is restricted, it may decrease demand for the cryptocurrency, leading to a drop in its price. Conversely, if a country is sanctioned and forced to rely on cryptocurrencies for trade and financial transactions, it may lead to an increase in demand for the cryptocurrency, leading to a rise in its price.
Impact on Crypto Exchanges and Wallets
Crypto sanctions can also impact crypto exchanges and wallets by limiting the ability of sanctioned parties to access these platforms. This can lead to a reduction in the availability of these services and an increase in the cost of using them.
Effect on National Security and Foreign Policy
Crypto sanctions can also have implications for national security and foreign policy to a great extent
- Use of Crypto Sanctions as a tool for Diplomacy: Crypto sanctions can be used as a tool for Diplomacy by governments to pressure other countries to change their behaviour. By limiting the ability of sanctioned parties to access financial systems and engage in international trade, governments can force other countries to comply with their demands or face further sanctions.
- Impact on Global Financial Markets: Crypto sanctions can also impact global financial markets by creating uncertainty and volatility. This can lead to reduced investor confidence and the availability of credit and other financial services.
Case studies: Examples of crypto sanctions
This section explores three examples of countries that have used cryptocurrencies to circumvent traditional economic sanctions. These case studies highlight the various ways cryptocurrencies can be used to evade sanctions and the challenges governments face in trying to regulate this emerging area.
Venezuela and Petro
In 2018, Venezuela launched its cryptocurrency, the Petro, backed by its oil reserves. The Petro was intended for Venezuela to bypass US sanctions and international access to capital. However, the US government quickly sanctioned Petro, making it illegal for US citizens and companies to buy or trade cryptocurrency. Despite these sanctions, some investors continued to buy and trade the Petro, with some claiming they could do so anonymously.
Iran and cryptocurrency mining
In 2019, the Iranian government legalized cryptocurrency mining to boost the country’s economy, which had been hit hard by US sanctions. Cryptocurrency mining involves using computer power to solve complex mathematical problems and earn rewards in the form of cryptocurrency. By legalizing cryptocurrency mining, Iran hoped to attract international investors and generate much-needed revenue. However, the US government also began sanctioning Iranian cryptocurrency mining operations, making it illegal for US citizens and companies to engage in these activities.
North Korea and crypto theft
North Korea has been accused of using cyber attacks to steal cryptocurrency from other countries, which it then uses to fund its nuclear weapons program. In 2019, a UN report found North Korea had stolen an estimated $2 billion in cryptocurrency through cyber attacks on exchanges and other financial institutions. The US government has also sanctioned several North Korean individuals and companies believed to be involved in these activities.
These case studies demonstrate the challenges that governments face in trying to regulate cryptocurrency and prevent it from being used to circumvent traditional economic sanctions. Cryptocurrencies are difficult to track and regulate and can be used anonymously, making it challenging for governments to enforce sanctions and prevent illicit activities. As such, using cryptocurrencies in sanctions evasion is likely to remain a persistent challenge for governments and financial institutions worldwide.
Challenges and criticisms of crypto sanctions
Several challenges and criticisms are associated with using cryptocurrency as a tool for imposing economic sanctions. These challenges and criticisms can be broadly grouped into three categories: technical, political, ethical and humanitarian concerns.
Technical challenges
One of the biggest challenges associated with using cryptocurrency to impose economic sanctions is the technical difficulty of tracking and monitoring cryptocurrency transactions. Cryptocurrencies are designed to be anonymous and decentralized, which makes it difficult for governments and financial institutions to identify the individuals or entities involved in illicit activities. Additionally, using privacy coins and other privacy-enhancing technologies can make it even more difficult to track cryptocurrency transactions.
Political challenges
Another challenge associated with using cryptocurrency to impose economic sanctions is the potential for political backlash. Some countries may view cryptocurrency sanctions as an infringement on their sovereignty and may respond with counter-sanctions or other retaliatory measures. Additionally, there may be disagreements among different countries and international organizations about which activities should be sanctioned and how they should be enforced.
Ethical and humanitarian concerns
Finally, there are also ethical and humanitarian concerns associated with the use of cryptocurrency sanctions. In some cases, cryptocurrency sanctions may disproportionately harm ordinary citizens rather than the targeted individuals or entities. For example, if a country’s government imposes cryptocurrency sanctions on its citizens, it may prevent them from accessing essential goods and services only available through international trade.
Future of crypto sanctions
Despite the challenges and criticisms associated with using cryptocurrency as a tool for imposing economic sanctions, we will likely continue to see cryptocurrency sanctions in the future. As cryptocurrencies become more widely adopted and sophisticated tracking and monitoring technologies are developed, governments and financial institutions may be better equipped to enforce cryptocurrency sanctions.
Several potential future developments could impact the use of cryptocurrency sanctions. For example:
Potential expansion of crypto sanctions
It is possible that we will see an expansion of the use of cryptocurrency sanctions in the future as more countries and international organizations recognize the potential of cryptocurrency as a tool for imposing economic sanctions.
Role of cryptocurrency regulation
The role of cryptocurrency regulation in the future of cryptocurrency sanctions is also likely to be significant. As more countries develop regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrency, tracking and monitoring cryptocurrency transactions may become easier, making it more difficult for individuals and entities to evade sanctions.
Role of blockchain technology
Finally, the role of blockchain technology in the future of cryptocurrency sanctions is also worth considering. Blockchain technology has the potential to provide a more secure and transparent way of tracking and monitoring cryptocurrency transactions, which could make it easier for governments and financial institutions to enforce sanctions. Additionally, blockchain-based digital identity systems could prevent anonymity in cryptocurrency transactions, further strengthening the ability to enforce sanctions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Crypto Sanctions have become an increasingly important tool for governments to achieve their foreign policy and national security objectives. As a result, businesses and individuals must be aware of the legal implications of Crypto Sanctions and take steps to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations. Given the complexity and evolving nature of Crypto Sanctions, it is essential to seek the guidance of expert lawyers who have specialized knowledge in this area.
Expert lawyers can provide valuable insights and advice on navigating the legal and regulatory landscape surrounding Crypto Sanctions. They can help businesses and individuals understand the implications of Crypto Sanctions on their operations, transactions, and investments and devise strategies to mitigate legal risks and ensure compliance. By consulting expert lawyers, businesses and individuals can stay updated with the latest developments and changes in Crypto Sanctions regimes and avoid costly legal penalties and reputational damage.
In summary, the importance of seeking legal advice for compliance with Crypto Sanctions cannot be overstated. With the help of expert lawyers, businesses and individuals can protect themselves and their assets and navigate the complexities of Crypto Sanctions with confidence and ease.
LegaMart is a global legal platform designed to connect individuals, startups, and businesses with qualified lawyers across jurisdictions. With a mission to simplify cross-border legal services, LegaMart provides users with access to a diverse network of vetted legal professionals who specialize in areas such as international law, corporate law, immigration, dispute resolution, and more.
By leveraging technology and user-friendly tools, LegaMart allows clients to search for lawyers by country, language, or legal expertise, submit their legal queries, and receive tailored legal solutions in a streamlined, efficient manner. The platform serves as a bridge between legal professionals and clients who need multilingual, multi-jurisdictional support — especially in today’s increasingly globalized legal landscape.
Whether you’re an entrepreneur launching a business abroad, an individual dealing with immigration paperwork, or a company navigating cross-border compliance, LegaMart aims to make legal help more accessible, transparent, and collaborative.




